Intel CPUs stability issue: Difference between revisions
m add categories |
m added a link |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- Creator's note: This is my first article, it needs work for sure, contact me if it needs revision. --> | <!-- Creator's note: This is my first article, it needs work for sure, contact me if it needs revision. --> | ||
This article discusses the stability issues related to Intel's 13th and 14th generation desktop processors, and how the company has handled the situation. | This article discusses the stability issues related to [[Intel]]'s 13th and 14th generation desktop processors, and how the company has handled the situation. | ||
==The problem== | ==The problem== | ||
Some users have reported system crashes, freezes, and instability during intensive workloads, particularly in applications that require high CPU usage. At first, the exact causes of this problem were unclear, prompting Intel to investigate and release official statements. | Some users have reported system crashes, freezes, and instability during intensive workloads, particularly in applications that require high CPU usage. At first, the exact causes of this problem were unclear, prompting Intel to investigate and release official statements. | ||
== Intel's response == | ==Intel's response== | ||
=== First statement === | ===First statement=== | ||
While the root cause of the problem was still unknown, part of it seemed to be caused by CPUs operating beyond recommended voltage, frequency, and thermal limits. According to Intel, most of the reports involve unlocked motherboards with BIOS settings that disable safeguards like '''Current Excursion Protection (CEP)''' and '''Thermal Velocity Boost (TVB)'''. Some motherboard manufacturers were also modifying the '''CPU load line''' configuration settings by default, optimizing it in order to make the processors run cooler. | While the root cause of the problem was still unknown, part of it seemed to be caused by CPUs operating beyond recommended voltage, frequency, and thermal limits. According to Intel, most of the reports involve unlocked motherboards with BIOS settings that disable safeguards like '''Current Excursion Protection (CEP)''' and '''Thermal Velocity Boost (TVB)'''. Some motherboard manufacturers were also modifying the '''CPU load line''' configuration settings by default, optimizing it in order to make the processors run cooler. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
'''Intel® will be publishing a public statement regarding issue status and Intel® recommended BIOS setting recommendations targeted for May 2024.'''</blockquote> | '''Intel® will be publishing a public statement regarding issue status and Intel® recommended BIOS setting recommendations targeted for May 2024.'''</blockquote> | ||
=== Second statement === | ===Second statement=== | ||
After conducting analysis on the returned chips, Intel has determined that instability issues were caused by elevated operating voltage, stemming from a microcode algorithm that generated incorrect voltage requests. Customer support was organized as follows: users who purchased systems from OEMs or system integrators were directed to contact their vendor, those with boxed processors were advised to reach out to Intel Support, and tray processor users were instructed to contact their place of purchase. | After conducting analysis on the returned chips, Intel has determined that instability issues were caused by elevated operating voltage, stemming from a microcode algorithm that generated incorrect voltage requests. Customer support was organized as follows: users who purchased systems from OEMs or system integrators were directed to contact their vendor, those with boxed processors were advised to reach out to Intel Support, and tray processor users were instructed to contact their place of purchase. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
==== Statement update ==== | ====Statement update==== | ||
The PR department subsequently updated the statement on [https://www.reddit.com/r/intel/comments/1e9mf04/intel_core_13th14th_gen_desktop_processors/ Reddit], integrating crucial details. A via oxidation manufacturing issue affected some early 13th Gen desktop processors, and it was resolved with improvements and screens in 2023. Analysis of instability reports seemed to indicate that a small percentage of cases were linked to this defect. It has also been confirmed that mobile 13th and 14th generation processors are not affected by any of these issues.<blockquote>So that you don't have to hun down the answer -> '''Questions about manufacturing or Via Oxidation as reported by Tech outlets:''' | The PR department subsequently updated the statement on [https://www.reddit.com/r/intel/comments/1e9mf04/intel_core_13th14th_gen_desktop_processors/ Reddit], integrating crucial details. A via oxidation manufacturing issue affected some early 13th Gen desktop processors, and it was resolved with improvements and screens in 2023. Analysis of instability reports seemed to indicate that a small percentage of cases were linked to this defect. It has also been confirmed that mobile 13th and 14th generation processors are not affected by any of these issues.<blockquote>So that you don't have to hun down the answer -> '''Questions about manufacturing or Via Oxidation as reported by Tech outlets:''' | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
=== Third statement === | ===Third statement=== | ||
The issues mentioned above have led to some CPUs becoming irreversibly damaged, resulting in the '''Vmin shift'''. High operating temperatures cause the silicon in the processor to degrade, requiring a higher minimum voltage to operate stably. This, in turn, leads to even higher temperatures, creating a vicious cycle that ultimately results in the CPU failing. Intel has identified four key issues contributing to the instability. For the explanation of each issue, refer to the full statement below. | The issues mentioned above have led to some CPUs becoming irreversibly damaged, resulting in the '''Vmin shift'''. High operating temperatures cause the silicon in the processor to degrade, requiring a higher minimum voltage to operate stably. This, in turn, leads to even higher temperatures, creating a vicious cycle that ultimately results in the CPU failing. Intel has identified four key issues contributing to the instability. For the explanation of each issue, refer to the full statement below. | ||
| Line 138: | Line 138: | ||
*Intel's 10-K pdf: https://www.intc.com/filings-reports/annual-reports/content/0000050863-24-000010/0000050863-24-000010.pdf | *Intel's 10-K pdf: https://www.intc.com/filings-reports/annual-reports/content/0000050863-24-000010/0000050863-24-000010.pdf | ||
*Link to the article going over AMD's growth in market share: https://www.tomshardware.com/pc-components/cpus/amds-desktop-pc-market-share-skyrockets-amid-intels-raptor-lake-crashing-scandal-amd-makes-biggest-leap-in-recent-history | *Link to the article going over AMD's growth in market share: https://www.tomshardware.com/pc-components/cpus/amds-desktop-pc-market-share-skyrockets-amid-intels-raptor-lake-crashing-scandal-amd-makes-biggest-leap-in-recent-history | ||
[[Category:Incidents]] | [[Category:Incidents]] | ||
[[Category:Articles based on videos]] | [[Category:Articles based on videos]] | ||
[[Category:Intel]] | [[Category:Intel]] | ||
Revision as of 17:39, 28 January 2025
This article discusses the stability issues related to Intel's 13th and 14th generation desktop processors, and how the company has handled the situation.
The problem
Some users have reported system crashes, freezes, and instability during intensive workloads, particularly in applications that require high CPU usage. At first, the exact causes of this problem were unclear, prompting Intel to investigate and release official statements.
Intel's response
First statement
While the root cause of the problem was still unknown, part of it seemed to be caused by CPUs operating beyond recommended voltage, frequency, and thermal limits. According to Intel, most of the reports involve unlocked motherboards with BIOS settings that disable safeguards like Current Excursion Protection (CEP) and Thermal Velocity Boost (TVB). Some motherboard manufacturers were also modifying the CPU load line configuration settings by default, optimizing it in order to make the processors run cooler.
Official statement (April 27, 2024):
Intel® has observed that this issue may be related to out of specification operating conditions resulting in sustained high voltage and frequency during periods of elevated heat.
Analysis of affected processors shows some parts experience shifts in minimum operating voltages which may be related to operation outside of Intel® specified operating conditions.
- While the root cause has not yet been identified, Intel® has observed the majority of reports of this issue are from users with unlocked/overclock capable motherboards.
- Intel® has observed 600/700 Series chipset boards often set BIOS defaults to disable thermal and power delivery safeguards designed to limit processor exposure to sustained periods of high voltage and frequency, for example: – Disabling Current Excursion Protection (CEP) – Enabling the IccMax Unlimited bit – Disabling Thermal Velocity Boost (TVB) and/or Enhanced Thermal Velocity Boost (eTVB) – Additional settings which may increase the risk of system instability: – Disabling C-states – Using Windows Ultimate Performance mode – Increasing PL1 and PL2 beyond Intel® recommended limits
Intel® requests system and motherboard manufacturers to provide end users with a default BIOS profile that matches Intel® recommended settings.
- Intel® strongly recommends customer’s default BIOS settings should ensure operation within Intel’s recommended settings.
- In addition, Intel® strongly recommends motherboard manufacturers to implement warnings for end users alerting them to any unlocked or overclocking feature usage.
Intel® is continuing to actively investigate this issue to determine the root cause and will provide additional updates as relevant information becomes available.
Intel® will be publishing a public statement regarding issue status and Intel® recommended BIOS setting recommendations targeted for May 2024.
Second statement
After conducting analysis on the returned chips, Intel has determined that instability issues were caused by elevated operating voltage, stemming from a microcode algorithm that generated incorrect voltage requests. Customer support was organized as follows: users who purchased systems from OEMs or system integrators were directed to contact their vendor, those with boxed processors were advised to reach out to Intel Support, and tray processor users were instructed to contact their place of purchase.
Official statement (July 22, 2024):
Based on extensive analysis of Intel Core 13th/14th Gen desktop processors returned to us due to instability issues, we have determined that elevated operating voltage is causing instability issues in some 13th/14th Gen desktop processors. Our analysis of returned processors confirms that the elevated operating voltage is stemming from a microcode algorithm resulting in incorrect voltage requests to the processor.
Intel is delivering a microcode patch which addresses the root cause of exposure to elevated voltages. We are continuing validation to ensure that scenarios of instability reported to Intel regarding its Core 13th/14th Gen desktop processors are addressed. Intel is currently targeting mid-August for patch release to partners following full validation.
Intel is committed to making sure all customers who have or are currently experiencing instability symptoms on their 13th and/or 14th Gen desktop processors are supported in the exchange process.
To help streamline the support process, Intel's guidance is as follows:
- For users who purchased 13th/14th Gen-powered desktop systems from OEM/System Integrator - please reach out to your system vendor's customer support team for further assistance.
- For users who purchased boxed 13th/14th Gen desktop processors - please reach out to Intel Customer Support for further assistance.
- For users who purchased tray 13th/14th Gen desktop processors - please reach out to your place of purchase for further assistance.
Statement update
The PR department subsequently updated the statement on Reddit, integrating crucial details. A via oxidation manufacturing issue affected some early 13th Gen desktop processors, and it was resolved with improvements and screens in 2023. Analysis of instability reports seemed to indicate that a small percentage of cases were linked to this defect. It has also been confirmed that mobile 13th and 14th generation processors are not affected by any of these issues.
So that you don't have to hun down the answer -> Questions about manufacturing or Via Oxidation as reported by Tech outlets:
Short answer: We can confirm there was a via Oxidation manufacturing issue (addressed back in 2023) and that only a small number of instability reports can be connected to the manufacturing issue.
Long answer: We can confirm that the via Oxidation manufacturing issue affected some early Intel Core 13th Gen desktop processors. However, the issue was root caused and addressed with manufacturing improvements and screens in 2023. We have also looked at it from the instability reports on Intel Core 13th Gen desktop processors and the analysis to-date has determined that only a small number of instability reports can be connected to the manufacturing issue.
For the Instability issue, we are delivering a microcode patch which addresses exposure to elevated voltages which is a key element of the Instability issue. We are currently validating the microcode patch to ensure the instability issues for 13th/14th Gen are addressed.
Question about Mobile 13th/14th Gen Stability issues
So, from what we have seen on our analysis of the reported Intel Core 13th/14th mobile products we have seen that mobile products are not exposed to the same issue. The symptoms being reported on 13th/14th Gen mobile systems – including system hangs and crashes – are symptoms stemming from a broad range of potential software and hardware issues.
As always, if you are experiencing issues with their Intel-powered laptops we encourage them to reach out to the system manufacturer for further help.
I'll be on the thread for the next couple of hours trying to address any questions you folks might have. Please keep in mind that I won't be able to answer every question but I'll do my best to address most of them.
Thanks
Lex H. - Intel
Edits:
- Added answers to Oxidation questions and questions about Mobile Processors
- Clarified short answer on Oxidation to that "there is a small number of instability reports connected to the manufacturing issue," from "but it is not related to the instability issue."
- Link to Robeytech removed as this is not Intel's official guidance to test for the instability issue Intel Core 13th/14th Gen desktop processor instability issues. Intel is investigating options to easily identify affected processors on end user systems,
Third statement
The issues mentioned above have led to some CPUs becoming irreversibly damaged, resulting in the Vmin shift. High operating temperatures cause the silicon in the processor to degrade, requiring a higher minimum voltage to operate stably. This, in turn, leads to even higher temperatures, creating a vicious cycle that ultimately results in the CPU failing. Intel has identified four key issues contributing to the instability. For the explanation of each issue, refer to the full statement below.
Official statement (September 25, 2024)
Following extensive investigation of the Intel® Core™ 13th and 14th Gen desktop processor Vmin Shift Instability issue, Intel can now confirm the root cause diagnosis for the issue. This post will cover Intel’s understanding of the root cause, as well as additional mitigations and next steps for Intel® Core™ 13th and 14th Gen desktop users.
Vmin Shift Instability Root Cause
Intel® has localized the Vmin Shift Instability issue to a clock tree circuit within the IA core which is particularly vulnerable to reliability aging under elevated voltage and temperature. Intel has observed these conditions can lead to a duty cycle shift of the clocks and observed system instability.
Intel® has identified four (4) operating scenarios that can lead to Vmin shift in affected processors:
- Motherboard power delivery settings exceeding Intel power guidance. a. Mitigation: Intel® Default Settings recommendations for Intel® Core™ 13th and 14th Gen desktop processors.
- eTVB Microcode algorithm which was allowing Intel® Core™ 13th and 14th Gen i9 desktop processors to operate at higher performance states even at high temperatures. a. Mitigation: microcode 0x125 (June 2024) addresses eTVB algorithm issue.
- Microcode SVID algorithm requesting high voltages at a frequency and duration which can cause Vmin shift. a. Mitigation: microcode 0x129 (August 2024) addresses high voltages requested by the processor.
- Microcode and BIOS code requesting elevated core voltages which can cause Vmin shift especially during periods of idle and/or light activity. a. Mitigation: Intel® is releasing microcode 0x12B, which encompasses 0x125 and 0x129 microcode updates, and addresses elevated voltage requests by the processor during idle and/or light activity periods.
Regarding the 0x12B update, Intel® is working with its partners to roll out the relevant BIOS update to the public.
Intel’s internal testing comparing 0x12B microcode to 0x125 microcode – on Intel® Core™ i9-14900K with DDR5 5200MT/s memory1 - indicates performance impact is within run-to-run variation (ie. Cinebench* R23, Speedometer*, WebXPRT4*, Crossmark*). For gaming workloads on Intel® Core™ i9-14900K with DDR5 5600MT/s memory2, performance is also within run-to-run variation (ie. Shadow of the Tomb Raider*, Cyberpunk* 2077, Hitman 3: Dartmoor*, Total War: Warhammer III – Mirrors of Madness*). However, system performance is dependent on configuration and several other factors.
Intel® reaffirms that both Intel® Core™ 13th and 14th Gen mobile processors and future client product families – including the codename Lunar Lake and Arrow Lake families - are unaffected by the Vmin Shift Instability issue. We appreciate our customers’ patience throughout the investigation, as well as our partners’ support in the analysis and relevant mitigations.
Next Steps
For all Intel® Core™ 13th/14th Gen desktop processor users: the 0x12B microcode update must be loaded via BIOS update and has been distributed to system and motherboard manufacturers to incorporate into their BIOS. Intel is working with its partners to encourage timely validation and rollout of the BIOS update for systems currently in service. This process may take several weeks.
Users can check their system/motherboard manufacturer’s website and/or the Intel® Product Compatibility Tool to see the latest BIOS versions for their Intel® Core™ 13th and/or 14th Gen-powered desktop systems: https://compatibleproducts.intel.com/.
- Processor: Intel® Core™ i9-14900K, Motherboard: Intel Raptor Lake Reference Board (M40919), Memory: 64GB DDR5 at 5200MT/s, Storage: ADATA* SU360, Graphics: Intel® UHD Graphics 770, Graphics Driver Version: 32.0.101.5768, Display Resolution: 1280x800, Operating System: Windows 11 Pro (version 26100.712).
- Processor: Intel® Core™ i9-14900K, Motherboard: Intel Raptor Lake Reference Board (RVP SR19), Memory: 32GB DDR5 at 5600MT/s, Storage: Samsung* 990 Pro 1TB, Graphics: MSI* RTX 4090 Suprim X, Graphics Driver Version: NVIDIA* v555.99, Resolution: 1920x1080, Operating System: Windows 11 (version 22631.4169)
Solutions
Here’s a summary of what owners of affected 13th and 14th Gen Intel CPUs can do:
- Update BIOS: Ensure the motherboard BIOS is updated to the latest version, incorporating Intel’s recommended default settings.
- Apply Microcode Updates: Install the latest microcode updates (0x125, 0x129, and 0x12B) to address voltage and performance state issues.
- Monitor Temperatures: Use adequate cooling solutions to prevent high operating temperatures, which can exacerbate instability.
- Avoid Overclocking: Stick to Intel’s recommended power and voltage limits to avoid stressing the CPU.
- Contact Support: If experiencing instability, reach out to customer support for assistance or potential replacements.
These steps can help mitigate instability and prolong the lifespan of the processor.
Broader implications
Over the past few years, Intel has faced numerous challenges, including competition from AMD, delays in its manufacturing process nodes, and a decline in its market share in key segments.
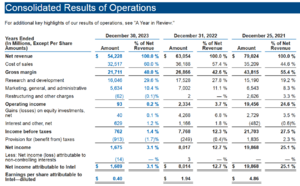
Revenue decline
Looking at the 10-K reports from recent years, a clear decline in net revenue, net income, and its percentage can be observed. The most alarming trend is the sharp drop in net income percentage, which plummeted from 25.1% in 2021 to just 3.1% in 2023.
Instability issues have further damaged the company image for reliability, potentially leading to higher costs and contributing to the already negative revenue trend.
According to reports from Mercury Research, AMD's market share for desktop CPUs in Q3 2024 was 9.6% higher compared to Q3 of the prior year. This growth could lead to a shift in market dynamics, potentially putting the competition at risk. Competition is essential for consumers because it drives companies to deliver better performance, efficiency, and value.
Intel's loss in market share highlights the importance of competition for innovation. However, with only two major CPU manufacturers, Intel and AMD, a significant imbalance in market share could limit consumer choice and innovation in the long run. Ensuring healthy competition between both players remains crucial for a balanced and thriving market.
Sources
- Link to first statement's article: https://www.igorslab.de/en/intel-releases-the-13th-and-14th-generation-k-sku-processor-instability-issue-update/
- Link to the official second statement: https://community.intel.com/t5/Processors/July-2024-Update-on-Instability-Reports-on-Intel-Core-13th-and/m-p/1617113
- Link to the modified reddit post of the second statement: https://www.reddit.com/r/intel/comments/1e9mf04/intel_core_13th14th_gen_desktop_processors/
- Link to the third statement: https://community.intel.com/t5/Blogs/Tech-Innovation/Client/Intel-Core-13th-and-14th-Gen-Desktop-Instability-Root-Cause/post/1633446#M40
- Intel's 10-K pdf: https://www.intc.com/filings-reports/annual-reports/content/0000050863-24-000010/0000050863-24-000010.pdf
- Link to the article going over AMD's growth in market share: https://www.tomshardware.com/pc-components/cpus/amds-desktop-pc-market-share-skyrockets-amid-intels-raptor-lake-crashing-scandal-amd-makes-biggest-leap-in-recent-history
