Apple
| Basic information | |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1976 |
| Legal Structure | Public |
| Industry | Electronics |
| Official website | https://apple.com/ |
Apple is an American technology company that was founded in 1976 by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak and Ronald Wayne. It is best known for its consumer electronics, software, and services.
Apple's current product lineup includes hardware such as the iPhone, iPad, Apple Watch, Mac, Apple Vision Pro, AirPods, and Apple TV; operating systems such as iOS, iPadOS, visionOS, and macOS; and various software and services including Apple Pay, iCloud, Apple Arcade, and multimedia streaming services like Apple Music and Apple TV+.
Incidents
[edit | edit source]Repairability of Apple products in the 2000s
[edit | edit source]Since the 2000s, Apple has focused on reducing the weight of its products as technology has advanced and become increasingly complex. This shift has contributed to challenges in repairing and upgrading their devices.
Hardware design issues in the 2010s
[edit | edit source]Apple had numerous hardware design issues in the 2010s, often poorly acknowledged by the company and frequently charging exorbitant amounts for repair.
- High-cost GPU failures on early 2010's MacBooks
- the 2016-'17 MacBook Pro's screen cable skimping scandal
- 2016-2019 MacBooks butterfly keyboards
- the 2019 16-inch MacBook Pro's SSD failures
- The announcement and cancellation of Apple AirPower due to overheating
Recent attempts to do better
[edit | edit source]Recently, Apple has made efforts to improve its products, though some observers feel that its pro-consumer practices still do not match those of certain other manufacturers. This shift is thought by some to be influenced by evolving legislation.
This includes:
- Opening an online Self Service Repair parts store.
- Making the back glass of iPhones removable starting from iPhone 14.
- Allowing alternative app stores in an update to iOS 17, in compliance with new EU legislation.
- Calibration tools for newly installed used parts in iOS 18, which sometimes work.
- An upgradeable, swappable SSD in the 2024 Mac Mini - albeit you cannot swap these units between M4 and M4 Pro units due to the internal casing's design being different without much good reason.
- A battery removable with just a 9V battery in the 2024 iPhone 16 and iPhone 16 Plus.
Many of these items have sparked allegations of Malicious Compliance and being introduced purely to make stricter right for repair legislation appear unnecessary to legislators while not doing much to improve the situation for consumers.
For instance, pricing for parts on the Self Service Repair store is virtually identical to having the part replaced by Apple themselves (including both the price of the part and labor), alternate app installation options are limited to users in the EU, still require developers to be registered with Apple, have them approve the apps and in many cases paying them fees, and the upgradeable SSDs do not use common standards such as M.2 NVME. Unlike standard SSDs, they are also not always swappable between different models and require access to a second Apple computer to provision after installation.
Operating system downgrades
[edit | edit source]It is not possible to upgrade or downgrade an iPhone, iPad, Apple TV, etc. to an Operating System (OS) version that is no longer signed by Apple. In most cases, only the most recent version is signed. Some exceptions exist, such as certain Apple TV models and Apple Silicon Macs. Downgrading the Apple TV 4K series is not possible at all due to the lack of a USB port. On Macs with T2 chip or Apple Silicon, the user can select from three modes of secure boot:[1]
- No security: Allow any OS to run (same as turning off secure boot on a PC).
- Medium security: Allow any OS that is signed with a secure boot certificate (default, same as turning on secure boot on a PC).
- Full security: Only allow the latest version of macOS, do not allow any other OS.
iOS devices only support full security mode. The device checks for a cryptographic "ticket," which are tied to the OS version and CPU serial number. These are provided by a server, which only provides them for the latest version (with very specific exceptions). The device refuses to boot if the ticket does not match. Workarounds exist, but with major caveats that are not viable for most users, see the technical details on SHSH blobs.
Class action lawsuit
[edit | edit source]Apple was the defendant of a class-action lawsuit with claims dating back to 2017 where users noticed their phones were being artificially slowed down. Apple agreed to settle the lawsuit for up to $500 million USD.[2] Apple claimed that this change was to benefit users who have old failing batteries, and that it wasn't for planned obsolescence. They later published software updates and an article explaining how users can opt out of this new "performance management" mode.[3]
Once a new OS version is installed, there is no opportunity to go back. This also restricts the user's choice to jailbreak the device, as the latest version naturally has patches for the latest jailbreak exploits. App developers also require access to earlier iOS versions to test that their app works correctly. The alternative, Xcode's iOS Simulator, is not a complete replacement for real hardware, as it does not have all features of a physical device.[4] Instead, app developers are forced to purchase several test devices, and remember to never allow them to update.
Parts availability
[edit | edit source]Many parts are not available directly from Apple. Those that are available directly from Apple may be more expensive than paying Apple to repair your device. Parts available to certified repair centers are extremely limited. Apple does not stock current generation iPad parts within GSX (See Certified Repair Centers). A limited selection of iPad parts are available from iFixit, however this can exclude some flex PCBs necessary for repairing headphone jacks.
If an Apple iPhone has GPS calibration issues and or Bluetooth connectivity issues, Apple will do their own diagnostics. You explain to the Apple employee how and when the issues occur and you explain in detail your methods to reproduce the issues. The issues occur when your phone is in your pocket while using navigation and when you hold your phone upside down while using your Apple Beats wireless headphones. After Apple runs their diagnostics and they are not able to detect the issues, they will move onto the next step which is fully resetting your device. This is considered a standard troubleshooting procedure. When you ask the Apple store manager if they would be willing to exchange your device for a similar model if they cannot fix your device they respond with "No, because these phones are designed to be fixed". After the software reset fail, Apple will require you to leave your phone with them so they can send it to their offsite repair facility for further diagnostics. After a few days, Apple will come to the conclusion that your phone requires an entire new midsection. When asked what was replaced, Apple will inform you that the entire inside has been replaced — essentially giving you a new phone (with a new IMEI, EID, etc.) apart from the casing and screen.
Diagnostic software availability
[edit | edit source]Calibration software for some Apple devices has only recently become available to end users. End user calibration tools have only become accessible in iOS 18. Similar calibration tools have been available to Certified Repair Centers, but are generally limited as many parts are serialized, i.e. lid sensors on Mac Books.
Certified repair centers
[edit | edit source]Certified Repair Centers have some limited access to Apple's proprietary backend (GSX2). GSX contains many tools necessary to repair devices such as diagnostic tools, calibration tools, parts catalog, and device repair history. GSX is only accessible to repair centers Apple deems certified. GSX does not stock parts for iPads. It does not allow the calibration of parts such as lid sensors for a device, if that device does not have an open repair and purchased parts. The new iOS 18 calibration tool is very similar to Apple's ASU (GSX's diagnostic/calibration tool). Some videos of GSX can be found online. See: GSX - How to Gain GSX Apple Access - iOSGenius
Advertisements in first party apps
[edit | edit source]In 2014, Apple and the band U2 partnered to give all iTunes users a free digital copy of their newest album at the time, Songs of Innocence, which was marketed as "the biggest album release ever in history".[5] Many users who didn't want the album couldn't remove it from their iTunes library due to the album being listed as a "past purchase" on their account (however the album could always be "hidden").[6] Some reports speculated the deal was worth 100 million dollars and was done due to the band's declining popularity.[7] In 2022, Bono, a member of U2, wrote in his memoir how Tim Cook reportedly said how "there’s something not right about giving [U2's] art away for free" and "the whole point of what we’re trying to do at Apple is to not give away music free. The point is to make sure musicians get paid".[8]
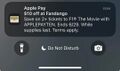
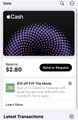
In 2025, Apple added a promotional offer for the F1 movie in their Wallet application. Users have mentioned how this could violate Apple's own policy on advertising, how the high price of Apple devices shouldn't justify first party ads, and the annoyance of seeing it.[9] For users on the iOS 26 beta, there is an option to disable "Offers & Promotions", with users on iOS 18 needing to disable notifications completely for the Wallet app.[10]
AirDrop censorship (2022)
[edit | edit source]As a result of the 2019 Hong Kong protests, Apple was pressured by the Chinese government to set a time limit for the AirDrop "everyone" option for iPhones due to its impact at scheduling protests against the government to avoid censorship.[11]
In 2023, the setting was applied to all iPhones worldwide to "mitigate unwanted file sharing", meaning users will need to set their airdrop setting manually every ten minutes instead of leaving it on permanently, leaving the only other options as "contacts only" and "receiving off".[12]
2024 Antitrust Lawsuit
[edit | edit source]In March 2024, the United States Department of Justice filed a lawsuit against Apple claiming that the "closed garden" ecosystem Apple creates surrounding its iPhones stifles competition and innovation. The lawsuit alleges that Apple is directly forcing customers to purchase and use iPhones and their accessories and software in several ways:
- Forcing mobile carriers including AT&T, Verizon, and T-Mobile to offer its best customer deals exclusively to those who purchase iPhones.
- Restricting the functionality of Super apps such as WeChat.
- Forcing in-app purchases through applications such as Fortnite to be made within the App Store and taking a part of the proceeds as commission pay.
- Restricting the use of third-party digital wallets and requiring users to exclusively use Apple Pay.
- Restricting how third-party message apps can interact with iMessage.
- Restricting their HomeKit home automation system and all compatible devices to work only on Apple's products and issuing cease & desist orders against emulators designed to make HomeKit compatible with third-party products.
- Restricting compatibility of third party smart watches.
Apple is expected to go to trial in early 2027.[13]
European Union USB-C Directive 2022/2380
[edit | edit source]As part of Directive (EU) 2022/2380, the EU mandated that all smartphones, tablets, digital cameras, headphones, and other portable electronic devices must utilize USB-C as a universal charging standard by the end of 2024, with laptops following by 2026. [14]
This regulatory measure directly addresses consumer frustration with incompatible chargers types and aims to significantly reduce electronic waste. [15] The legislation allows manufacturers to unbundle chargers from devices, potentially saving consumers money, and ensures charging speed harmonization across compatible devices.
While Apple initially opposed the standardization, arguing that it would "stifle innovation rather than encourage it," the company ultimately conceded defeat, with Apple's head of marketing stating "we have no choice" regarding compliance. [16]
European Digital Markets Act.
[edit | edit source]This law forced many companies including Apple to change the way they operate to create a fairer competition. Read more about this law here.
Changes Apple introduced iOS and iPadOS to comply with this law:
[edit | edit source]- Introduced the ability to install applications from alternative marketplaces
- asks which browser and search engine should be the default one
- Developers now are allowed to publish in the EU browsers that do not use webkit
Controversies:
[edit | edit source]- Apple removed iPhone torrenting app iTorrent from alternative marketplace AltStore PAL, developer said that the access was revoked "without any warning". In a statement to The Verge, Apple spokesperson Peter Ajemian said, “Notarization for this app was removed in order to comply with government sanctions-related rules in various jurisdictions. We have communicated this to the developer.”[17]
Elon Musk Lawsuit
[edit | edit source]In August of 2025, businessman Elon Musk accused Apple of engaging in anti-competitive practices by only allowing their AI program OpenAI to reach the top of the sales chart on Apple App Store. He announced his plan to sue Apple for this practice.[18]
-
Notification of the offer
-
Home screen of Wallet app
-
Apple Cash card screen
-
Screen when selecting "learn more"
Greenwashing
[edit | edit source]Apple claims to be environmentally friendly and invests significant amounts of funds in corresponding PR campaigns,[19] but the reality is not quite as green.
Customers are lead to think that their purchases and frequent replacement of their devices do not have a negative impact on the environment, which is not the case.
Green energy sharing
[edit | edit source]Apple shares manufacturing capacity at Chinese/Taiwanese companies FoxConn and Pegatron with other companies. If Apple uses a hypothetical 20% of their manufacturing capacity, and company B, C, D, and E also each take up 20%, and the company doing the manufacturing runs on 20% renewably generated energy, now Apple as well as companies B, C, D, and E will each publicly claim that their manufacturing runs 100% on renewable energy. In other words, each company will claim the 20% renewable energy was used for their production.[20]
CO2 Certificates and forest projects
[edit | edit source]…
The packaging trick
[edit | edit source]Apple, like many companies, regularly emphasises how environmentally friendly their packaging is and highlight advancements in this area.[21]
This deliberately distracts from the fact that only a negligible fraction of the environmental footprint of an electronic device comes from the packaging, as it is made of siginificant amounts or rare earth minerals, metals and mined components and consuming vast amounts of energy, water and fuel in manufacturing and transport.
Some of the environmental advancements touted by Apple could also be argued to be environmentally beneficial side effects of purely economic decisions aimed at maximizing profit, such as shipping iPhones without chargers.[22]
Shredding vast amounts of fully functional devices
[edit | edit source]In 2020, it came to light that Apple had filed a lawsuit against a recycling company, revealing that 100 000 iPhones had been illegitimately shipped to China to be sold there instead of being shredded as had been agreed with Apple.[23][24]
These devices were likely trade-in devices from people who received a discount on a new model in exchange. Bloomberg News writes, referring to the contract with the recycler:[25]
Even if the iPhones looked good enough for resale, Apple Inc.’s contract with GEEP (said with a hard “g”) explicitly required that every product it sent be destroyed.
Used iPhone that are sold on the used market are a direct competition to new sales by Apple. Apple likely does not want the public to know about these processes, since security seems to be tight around the shredding process:
In some cases, Apple hired outside security consultants to escort trucks to its recyclers and monitor the destruction process, which the tech giant could further analyze through data reports charting scrap weights and commodity yields to ensure the input matched the output.[26]
Apple later retreated the lawsuit, most likely to avoid having to disclose how many devices they are really shredding.[26]
iPhone recycling robot mostly a publicity stunt
[edit | edit source]The first iteration of Apple's iPhone recycling robot, designed for the iPhone 6, was never more than a publicity stunt, according to an article by Bloomberg:[25]
Liam’s precision automation, however, proved a dead end. It could handle just one iPhone model, and not that well. If a device had corroded screws or sticky insides, the robot would glitch. A person familiar with the project estimates Liam could run for about 10 minutes without human intervention. Another person says Apple at times fed the robot still-functioning iPhones and, for media demos, cherry-picked cleaner units so it didn’t crash, suggesting Liam was geared more for promotion than scalability.
The same article cites industry insider claiming that the new iteration of the robot is only able to recycle as many devices in a year as Apple sells in just 48 hours.[25]
Thus it is safe to assume that the vast majority of trade-in devices are simply shredded.
Products
[edit | edit source]Software
[edit | edit source]See also
[edit | edit source]References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ "About Startup Security Utility on a Mac with the Apple T2 Security Chip". Apple. Archived from the original on 7 Jun 2025. Retrieved 22 Jun 2025.
- ↑ Cooper, Gael (9 Jan 2024). "Apple Starts Sending Out iPhone 'Batterygate' Settlement Payments. What to Know". CNET. Archived from the original on 21 Mar 2025. Retrieved 22 Jun 2025.
- ↑ "iPhone battery and performance". Apple. Archived from the original on 18 Jun 2025. Retrieved 22 Jun 2025.
- ↑ Vajpai, Shreeti (24 Jun 2024). "iOS Emulators / Simulators vs Real iOS Devices". ContextQA. Archived from the original on 19 May 2025. Retrieved 22 Jun 2025.
- ↑ "Apple & U2 Release "Songs of Innocence" Exclusively for iTunes Store Customers". Apple Newsroom. 2014-09-09. Archived from the original on 2025-04-05. Retrieved 2025-06-25.
- ↑ Assar, Vijith (2014-09-16). "Apple's Devious U2 Album Giveaway Is Even Worse Than Spam". WIRED. Archived from the original on 2025-05-30. Retrieved 2025-06-25.
- ↑ Rott, Nathan (2014-09-15). "Apple's U2 Album Promotion Backfires". NPR. Archived from the original on 2025-06-01. Retrieved 2025-06-25.
- ↑ Bove, Tristan (2022-10-24). "Apple CEO Tim Cook thought U2 putting its album on your iPhone was 'not right'—even though he did it anyway". Fortune. Archived from the original on 2025-01-27. Retrieved 2025-06-25.
- ↑ u/african-nightmare (2025-06-24). "Getting ads in Apple Wallet, how to disable?". Reddit. Retrieved 2025-06-25.
- ↑ Perez, Sarah (2025-06-24). "iPhone customers upset by Apple Wallet ad pushing 'F1' movie". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on 2025-06-24. Retrieved 2025-06-25.
- ↑ Weatherbed, Jess (2022-11-10). "Apple limits AirDrop in China after its use in protests". The Verge. Archived from the original on 2025-07-23. Retrieved 2025-08-24.
- ↑ Hall, Zac (2025-03-17). "Apple globally censoring this iPhone communication feature deserves renewed scrutiny". 9To5Mac. Archived from the original on 2025-07-23. Retrieved 2025-08-24.
- ↑ Liedtke, Michael (2025-06-30). "Judge allows antitrust lawsuit against Apple to proceed". Associated Press. Retrieved 2025-07-14.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ "Directive (EU) 2022/2380 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 November 2022 amending Directive 2014/53/EU on the harmonisation of the laws of the Member States relating to the making available on the market of radio equipment (Text with EEA relevance)". EUR-Lex. 2022. Retrieved 2025-09-02.
- ↑ "USB-C-Standard: Schluss mit dem Kabelwirrwarr". zdfheute. 2024-12-28. Retrieved 2025-09-02.
- ↑ "Apple to put USB-C connectors in iPhones to comply with EU rules". The Guardian. 2022-10.26. Retrieved 2025-00-02.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|access-date=and|date=(help) - ↑ Weatherbed, Jess (August 28, 2025). "Apple pulls iPhone torrent app from AltStore PAL in Europe". The Verge. Archived from the original on September 3, 2025.
- ↑ Durden, Tyler (2025-08-12). "Musk Accuses Apple Of "Unequivocal Antitrust Violation" For Favoring OpenAI In App Store Rankings". ZeroHedge. Retrieved 2025-08-14.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ "Environment | Mother Nature". Apple. Retrieved 2025-09-15.
- ↑ Gieselmann, Hartmut (2023). "Von wegen CO2-neutral – Umweltexperten werfen Apple Greenwashing vor". c't Magazin für Computertechnik [Germany]. 2023 (23): 49.
- ↑ "Apple 2030 – We've reduced our emissions by over 60%". Apple. Retrieved 2025-09-15.
- ↑ Dragan, Lauren (2023-09-12). "iPhones No Longer Come With a Charger or Headphones. Here's What to Get If You Need Them". The New York Times. Retrieved 2025-09-15.
- ↑ Lovejoy, Ben (2024-04-24). "100,000 iPhones stolen instead of scrapped; Apple accused of shredding usable devices". 9to5mac. Retrieved 2025-09-16.
- ↑ Carrique, Felicitas (2020-10-04). "Apple sues recycling partner for reselling more than 100,000 iPhones, iPads, and Watches it was hired to dismantle". The Verge. Retrieved 2025-09-16.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 Carr, Austin (2024-04-18). "What Really Happens When You Trade In an iPhone at the Apple Store". Bloomberg. Retrieved 2025-09-16.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Carr, Austin (2025-03-17). "Apple Drops Lawsuit Against Recycler in Mystery of Missing iPhones". Bloomberg News. Retrieved 2025-09-16.